- Home
- Machinery
- Metal Spinning Machines
- Flow Forming Machines
- Wheel Forming Machines
- Shear Forming Machines
- Necking-In / Closing Machines
- Rotary Forging Machines
- Pulley Forming Machines
- Trimming, Beading,… Machines
- Circular and Ring Shears
- Custom Machines and R&D
- Robotics, Loading & Unloading
- Upgrades – Used – Retrofits
- DENN Software / Technologies
- Machinery Technologies
- Applications & Industries
- Lubricants
- News & Updates
- Contact / Info / Service
- Home
- Machinery
- Metal Spinning Machines
- Flow Forming Machines
- Wheel Forming Machines
- Shear Forming Machines
- Necking-In / Closing Machines
- Rotary Forging Machines
- Pulley Forming Machines
- Trimming, Beading,… Machines
- Circular and Ring Shears
- Custom Machines and R&D
- Robotics, Loading & Unloading
- Upgrades – Used – Retrofits
- DENN Software / Technologies
- Machinery Technologies
- Applications & Industries
- Lubricants
- Blog
- Contact / Info / Service
Top 10 Best Deep Drawing Steel Techniques for Superior Metal Forming
Deep drawing steel is a vital process in the metal forming industry, renowned for its ability to create complex shapes from flat sheets of metal with remarkable efficiency and strength. Experts in the field, such as Dr. John H. Smith, a leading metallurgist with over two decades of experience, emphasize the importance of mastering deep drawing techniques. He once stated, “The effectiveness of deep drawing steel processes can significantly enhance product quality and reduce production costs when executed with precision.”
In this evolving industry, the demand for high-quality metal components continues to rise, compelling manufacturers to explore the best techniques for deep drawing. Understanding the nuances of this process not only aids in achieving superior formability but also plays a crucial role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of the final products. This article highlights the top ten techniques for optimizing deep drawing steel, providing valuable insights for professionals seeking to elevate their production methodologies and stay competitive in the market.
As we delve into these techniques, it will become evident that each method offers unique benefits and challenges. Through expert knowledge and innovative approaches, mastering deep drawing steel is essential for crafting exceptional metal parts tailored to meet the evolving needs of various industries.

Table of Contents
[Hide]
Understanding Deep Drawing Steel and Its Importance in Metal Forming
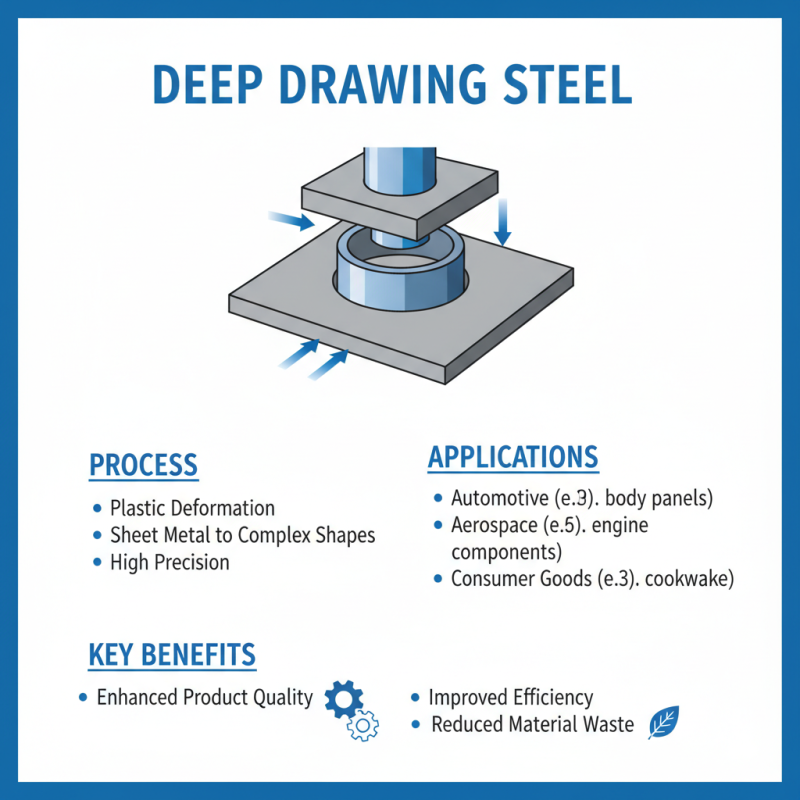
Deep drawing steel is a critical process in metal forming that enables the production of complex shapes with high precision. This technique involves the plastic deformation of sheet metal, often resulting in components that are essential in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Understanding the fundamentals of deep drawing steel is vital for engineers and manufacturers, as it not only enhances the quality of the final product but also improves efficiency and reduces waste during production.
The importance of deep drawing steel lies in its ability to achieve intricate geometries while maintaining the material's structural integrity. The process typically involves applying force through a punch that draws the metal into a die, allowing for the creation of deep, cupped shapes. Mastering the parameters such as material selection, lubrication, and process design can significantly impact the success of deep drawing operations. By utilizing advanced techniques and tools, manufacturers can optimize production processes, resulting in superior metal forming capabilities that meet the ever-evolving demands of the market.
Key Techniques in Deep Drawing for Enhanced Material Ductility
Deep drawing is a crucial process in metal forming, aimed at producing complex shapes with enhanced ductility. Key techniques in this discipline focus on optimizing material flow and minimizing defects during the drawing process. One fundamental approach is controlling the die geometry, which directly influences the material's behavior as it transitions from a flat blank to a formed part. A well-designed die can help distribute stress evenly across the material, reducing the likelihood of thinning or fracture.
Another important technique involves the use of lubricants that improve the surface interactions between the tool and the material. Effective lubrication reduces friction, allowing for smoother material movement and better surface finish. Additionally, adjusting the mechanical properties of the steel prior to the deep drawing process, such as through annealing, can enhance its ductility. This heat treatment allows the material to absorb more energy and deform more readily, leading to better outcomes in complex geometries. By combining these key techniques, manufacturers can achieve superior results in deep drawing, resulting in high-quality components that meet stringent performance specifications.
Top 10 Best Deep Drawing Steel Techniques for Superior Metal Forming
This chart illustrates the improvement in ductility for various deep drawing techniques. Each technique showcases its effectiveness in enhancing the material properties, which is crucial for successful metal forming processes.
Optimizing Tool Design for Effective Deep Drawing Processes
In the realm of metal forming, particularly in deep drawing processes, the design of tools plays a crucial role in optimizing performance and ensuring product quality. A well-thought-out tool design can significantly enhance the efficiency of production while minimizing defects. This involves considering various factors such as tool geometry, material selection, and surface treatments. The shape of the die and punch must be meticulously crafted to facilitate the metal's flow and reduce friction, which can lead to a smoother drawing process and improved dimensional accuracy.
Another essential aspect of optimizing tool design is the integration of advanced cooling and lubrication systems. Effective lubrication not only lessens wear and tear on the tools but also aids in maintaining the quality of the formed metal. Additionally, incorporating materials with high wear resistance can extend the lifespan of the tools and reduce downtime for maintenance. By utilizing simulation software, engineers can visualize the deep drawing process and make data-driven adjustments to tool designs, ensuring that they meet the specific requirements of the metal being formed. This proactive approach leads to more reliable outcomes and greater consistency in product quality, setting the foundation for superior metal forming techniques.
Top 10 Best Deep Drawing Steel Techniques for Superior Metal Forming - Optimizing Tool Design for Effective Deep Drawing Processes
| Technique | Description | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controlled Lubrication | Optimizing lubricant application to minimize friction | Reduces wear, improves surface quality | Requires precise control systems |
| Progressive Die Design | Utilizing multi-stage operations within a single die | Increased efficiency, reduced handling | Complex design and manufacturing |
| Forming Simulation Software | Using simulations to predict material behavior | Enhances design accuracy, reduces trial-and-error | Requires investment in software and training |
| Variable Blank Holder Force | Adjusting pressure on the blank during forming | Improves material flow, reduces wrinkling | Requires sophisticated control mechanisms |
| Heat Treatment | Applying heat cycles to enhance material properties | Improves ductility and strength | Process time and energy consumption |
| Multi-Axis Forming | Utilizing advanced machines for complex shapes | Greater design flexibility, increased design options | Higher machine costs, complex programming |
| Use of advanced alloys | Implementing stronger, lighter materials | Higher strength-to-weight ratio | Cost and availability of materials |
| Die Maintenance Protocols | Regular maintenance to ensure die integrity | Increases tool life and performance | Requires schedule and resources |
| Enhanced Design Iterations | Rapid prototyping to test designs quickly | Speeds up the development process | Possible increased costs |
| Precision Measurement Techniques | Utilizing advanced measuring tools to ensure specifications | Improves quality control, reduces defects | Investment in equipment and training needed |
Material Selection: Choosing the Right Steel for Deep Drawing
When selecting materials for deep drawing in metal forming processes, the choice of steel is pivotal to achieving high-quality results. Deep drawing involves the deformation of sheet metal into a desired shape, often requiring materials that exhibit excellent ductility and strength. According to industry reports, advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) have gained popularity due to their superior mechanical properties, enabling manufacturers to produce thinner and lighter components without compromising structural integrity. For instance, the World Steel Association highlights that using AHSS can reduce the weight of stamped parts by up to 25% while maintaining the necessary durability.
Moreover, the specific characteristics of different types of deep drawing steels must be carefully considered. Materials like stainless steel offer excellent corrosion resistance but may require specialized processing techniques. In contrast, low-carbon steels are often favored for their malleability, making them ideal for complex shapes. A study by the American Iron and Steel Institute states that low carbon content typically enhances shaping capabilities, with optimal carbon levels between 0.05% and 0.15% for deep drawing applications. Ultimately, the right material selection can significantly impact both the efficiency of the manufacturing process and the overall performance of the final product, making informed decisions critical in the metal forming industry.
Quality Control Measures in Deep Drawing Operations for Better Outcomes

In deep drawing operations, implementing stringent quality control measures is essential for achieving superior outcomes. According to a report by the Institute of Metal Forming Techniques, approximately 15% of defects in deep drawn products are attributed to inadequate quality control practices. This underscores the need for robust methodologies that can anticipate and mitigate common issues such as wrinkling, tearing, and dimensional inaccuracies. Advanced techniques such as real-time monitoring of material conditions and process parameters can significantly enhance the quality of the final product.
Furthermore, the introduction of statistical process control (SPC) in deep drawing processes allows manufacturers to systematically analyze variations in production. A study by the Society of Manufacturing Engineers indicated that organizations that adopted SPC saw a 30% reduction in defect rates over a two-year period. By investing in training for operators and ensuring compliance with standardized procedures, companies can foster a culture of quality that translates into improved efficiency and reduced waste. Through these quality control measures, deep drawing operations can achieve not only higher quality outputs but also better economic performance, ultimately leading to a competitive advantage in the manufacturing sector.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Best Metal Spinning Lathe Tools for Your Projects
-

2025 Top 5 Pipe Roll Forming Machines You Need to Know
-

What is Aluminium Spinning Machine and How Does it Work
-

What is a Steel Forming Machine? A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Its Uses and Benefits
-

10 Essential Tips for Optimizing Flow Forming Metal Techniques
-

The Essential Guide to Forming Metal: Techniques, Applications, and Market Insights in 2023
