- Home
- Machinery
- Metal Spinning Machines
- Flow Forming Machines
- Wheel Forming Machines
- Shear Forming Machines
- Necking-In / Closing Machines
- Rotary Forging Machines
- Pulley Forming Machines
- Trimming, Beading,… Machines
- Circular and Ring Shears
- Custom Machines and R&D
- Robotics, Loading & Unloading
- Upgrades – Used – Retrofits
- DENN Software / Technologies
- Machinery Technologies
- Applications & Industries
- Lubricants
- News & Updates
- Contact / Info / Service
- Home
- Machinery
- Metal Spinning Machines
- Flow Forming Machines
- Wheel Forming Machines
- Shear Forming Machines
- Necking-In / Closing Machines
- Rotary Forging Machines
- Pulley Forming Machines
- Trimming, Beading,… Machines
- Circular and Ring Shears
- Custom Machines and R&D
- Robotics, Loading & Unloading
- Upgrades – Used – Retrofits
- DENN Software / Technologies
- Machinery Technologies
- Applications & Industries
- Lubricants
- Blog
- Contact / Info / Service
Understanding the Roll Forming Process: Benefits and Applications Explained
The roll forming process is a highly efficient metal fabrication technique that involves the continuous bending of a long strip of sheet metal into desired shapes. This process has seen significant growth within the manufacturing sector, driven by its ability to produce consistent, high-quality components at rapid production speeds. According to a report by IBISWorld, the roll forming industry has experienced a steady annual growth rate of approximately 3.5% over the past five years, illustrating its increasing importance in various applications across construction, automotive, and appliance manufacturing.
One of the key advantages of the roll forming process is its capability to maintain tight tolerances and produce complex geometries without compromising material integrity. Furthermore, the National Association of Manufacturers states that over 90% of U.S. manufacturers utilize roll formed components in their production lines, highlighting its critical role in modern manufacturing. As industries evolve and the demand for precision-engineered products rises, understanding the benefits and applications of the roll forming process becomes essential for manufacturers aiming to optimize their operations and enhance product quality.
Table of Contents
[Hide]
Introduction to Roll Forming: Definition and Overview
Roll forming is a continuous bending operation that shapes metal sheets into specific profiles by passing them through a series of rollers. This process is widely used in industries ranging from construction to automotive due to its efficiency in producing lightweight, complex shapes with high precision. With the ability to handle a variety of materials including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, roll forming offers versatility that is essential for modern manufacturing.
According to a report by Grand View Research, the global roll forming market size was valued at approximately $8 billion in 2020, with expectations to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient building materials and automotive components that promote lightweight construction. Roll forming not only reduces material waste but also enhances production speed, making it a favorable choice for manufacturers looking to improve their operational efficiency.
Tips: When considering roll forming for your next project, it’s essential to analyze the material properties to determine the best forming methods. Additionally, working closely with your engineering team can lead to innovative designs that optimize the material's structural integrity, ensuring durability and performance. Lastly, regular maintenance of roll forming equipment can significantly extend its lifespan and maintain production quality.
Understanding the Roll Forming Process: Benefits and Applications
Key Advantages of the Roll Forming Process
The roll forming process is a highly efficient method of shaping metal into various profiles and sections. One of the key advantages of this process is its ability to produce complex shapes with a continuous length, which can significantly reduce material waste. This efficiency not only cuts costs but also minimizes the environmental impact by maximizing the use of raw materials. Additionally, roll forming can operate at high speeds, making it ideal for large-scale production runs, ensuring timely delivery and increased productivity for manufacturers.
Tip: When considering roll forming for your project, evaluate the required tolerances and the complexity of the desired shapes. This will help you choose the right specifications to maximize the benefits of this method.
Another notable advantage of roll forming is its versatility in applications across various industries, including construction, automotive, and furniture manufacturing. This process can easily accommodate different materials, such as steel, aluminum, and even certain plastics, adapting to the unique needs of different projects. Furthermore, roll-formed products exhibit superior strength and durability, making them suitable for structural applications where load-bearing capabilities are essential.
Tip: Always seek to optimize the design of your roll-formed parts to ensure that they meet performance criteria while keeping production costs as low as possible. This includes considering features like variable wall thickness and integrated stiffening elements.
Common Materials Used in Roll Forming
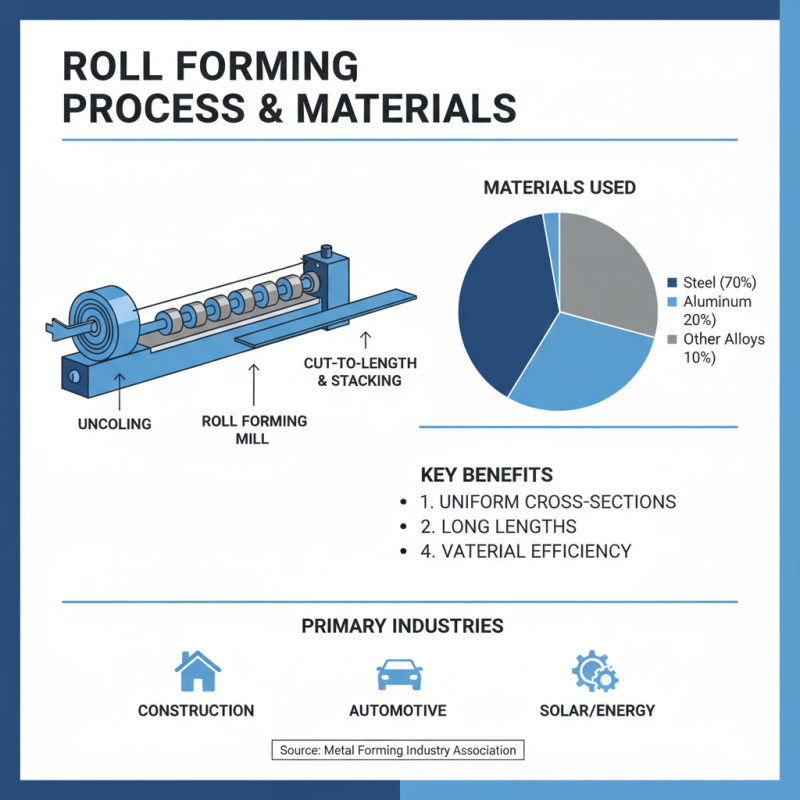
Roll forming is a versatile manufacturing process utilized in various industries, primarily for producing long lengths of metal parts with uniform cross-sections. A diversity of materials can be used in roll forming, contributing to its widespread application. Steel remains the material of choice due to its strength and availability, constituting approximately 70% of roll-formed products, as reported by the Metal Forming Industry Association. Other common materials include aluminum, known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, and various alloys that provide enhanced mechanical characteristics.
Besides steel and aluminum, plastics and composites are increasingly used in roll forming to benefit from their unique properties. The adoption of high-performance polymers, such as polycarbonate and PVC, is driven by their potential to reduce weight without sacrificing structural integrity, making them ideal for sectors like automotive and construction. According to recent industry analyses, the demand for roll-formed plastic components is projected to grow by 6% annually over the next five years.
**Tip:** When selecting material for roll forming, consider the application requirements such as weight, strength, and environmental resistance. This ensures optimal performance and longevity of the final product, particularly in demanding environments.
Applications of Roll Forming in Various Industries
Roll forming is a versatile manufacturing process used across various industries to create long, continuous shapes of metal with uniform cross-sections. Its efficiency and adaptability make it a popular choice for producing components in sectors like automotive, construction, and appliance manufacturing. For instance, in the automotive industry, roll forming is utilized to produce parts like frame rails and reinforcements, which are essential for vehicle integrity and safety. The process also enables the production of lightweight, high-strength components that contribute to overall fuel efficiency.
In the construction industry, roll forming is frequently employed to create structural elements such as metal studs, tracks, and roofing panels. These components are integral to building frameworks, providing durability and support while optimizing resource use. The versatility of roll forming allows for customization in design, ensuring that manufacturers can meet specific architectural requirements. Another notable application is in the creation of appliance parts, where roll formed parts are used for things like brackets and panels, providing both aesthetic appeal and functional robustness.
Tips: When considering roll forming for production, it’s essential to focus on material selection and yield strength to ensure the final products meet design specifications and performance standards. Additionally, collaborating closely with engineers during the design phase can help optimize the roll forming process, resulting in cost-effective production while maintaining high quality. Always evaluate the potential for automation in the roll forming setup to improve efficiency and reduce operational costs.
| Industry | Application | Material Used | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Chassis components | Steel, Aluminum | High strength-to-weight ratio |
| Construction | Roofing and siding | Galvanized Steel | Weather resistance and durability |
| HVAC | Ductwork | Aluminum, Stainless Steel | Energy efficiency and custom shapes |
| Furniture | Frames and supports | Mild Steel | Cost-effective and lightweight |
| Electrical | Cable trays | Steel | Strong support and ease of installation |
Comparison of Roll Forming with Other Metal Fabrication Techniques
When evaluating metal fabrication techniques, roll forming stands out for its unique advantages, particularly in the production of long lengths of uniform and complex shapes. Unlike traditional methods such as stamping and machining, which typically involve cutting material from larger sheets, roll forming utilizes a continuous bending operation. This process allows for a more efficient material usage, resulting in less waste and potentially lower costs. Moreover, roll forming can accommodate a wide variety of materials, including steel and aluminum, making it highly versatile for different applications.
In comparison, other techniques like stamping can be limited in the complexity of shapes they can produce, often requiring multiple operations to achieve similar results as roll forming. Machining, while precise, often involves slower production rates and increased labor costs due to more manual intervention. Roll forming's automated process allows for higher throughput and consistency, making it an ideal choice for mass production of components in industries such as construction, automotive, and HVAC systems.
This efficiency, combined with the ability to create intricate profiles, solidifies roll forming's position as a preferred method in the realm of metal fabrication.
Related Posts
-

Why Choose Metal Forming Inc for Your Manufacturing Needs
-

2025 Top Digital Metal Machining Equipment Trends You Need to Know
-

The Essential Guide to Forming Metal: Techniques, Applications, and Market Insights in 2023
-

2025 Top 5 Engineering Machinery Innovations Transforming the Industry
-

Top 5 Metal Roll Forming Machines for Precision Manufacturing in 2023
-

How to Use Flow Forming Steel for Maximum Strength and Durability
